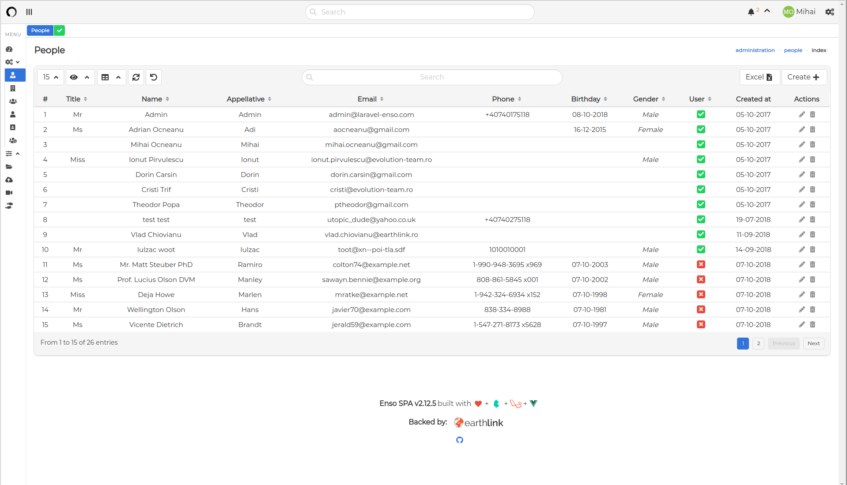
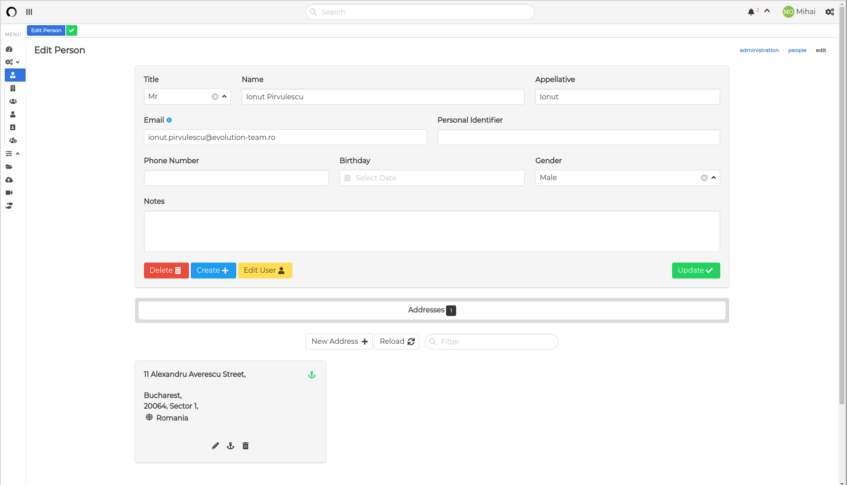
People
Person management dependency for Laravel Enso.
This package works exclusively within the Enso ecosystem.
The front end assets that utilize this api are present in the ui package.
For live examples and demos, you may visit laravel-enso.com
click on the photo to view a large size screenshot
Installation
Comes pre-installed in Enso.
Features
- separates the people centric operations from the core application user model
- allows the management of people and their details
- integrates with and extends the application user
- is built upon the premise that all the application users are people, but some people may not be application users
- can be reused and integrated with other modules which might handle categories of people (e.g. company people)
- a
PersonFactoryis included by default in the package - a policy is used to ensure that a person email update cannot be performed if the person is linked to an user
- custom validations may be added through the package configuration
- the people server-side select functionality is included by default
- the included
IsPersontrait can be used on other models that have apersonrelationship and require email synchronization - enums are used for person genders and titles
Usage
Backstory
In previous Enso versions, there was no common ground between application users and other categories of actors which also represented people, for example contacts and (some types of) clients. This sometimes lead to duplicated data as well as brittle and non reusable types and relationships.
In order to move towards better maintainability, the decision to move common data into persons was taken. Now the people structure can be reused as needed.
Under the Hood
- the model comes with a
hasUserhelper to check if this person is linked to an user - once the person has activity in the system (through any other model relationship), it cannot be deleted
- the proper way to delete a person is to first delete any other models it is linked to
- since an application user will always be a person, and for Laravel authentication purposes, the user is supposed to have an email address and so the 'synchronization' between the user and the person is required. Therefore, if the user email is updated, the person email is also updated. The same thing happens if a user is created from a person, but a different email is set.
- note that if users are created through a separate/external mechanism you will need to ensure that a corresponding person is created/available during the process
- all
Personattributes are fillable - the
uidPerson attribute is meant as generic holder for a person's unique identifier which varies from situation to situation (e.g. SSN) - the
Personmodel has the following helpers:hasUser- returns true if this person is associated to a usergender- determines the gender based on the set person title. If no title is set, null is returnedisMandatary- returns true if this user is set a company's mandatary
- the
PersonPolicyensures that:- administrators can make any changes
- a user can only set a
Configuration
The config/enso/people.php configuration file, lets you customize the following:
formTemplate, - string, is the project relative path to the person form template, useful for overriding the originaltableTemplate, - string, is the project relative path to the person table template, useful for overriding the original
Extending the people functionality
In your project you may have the need to alter and or extend the people structure by adding/removing table columns. To achieve this, you'd need to:
add migration(s) to your local project, making the necessary changes. Note that if using sqlite for testing, some of the migration commands may not be available
create a new template for the person form, and declare it in the config (
formTemplate)create a new template for the person table, and declare it in the config (
tableTemplate)create a new person request validation, as required, which should extends the Enso person validation
use LaravelEnso\Companies\app\Http\Requests\ValidatePersonStore as EnsoPersonStore; class ValidatePersonStore extends EnsoPersonStore ...create a new
Person, as required, which should extend the Enso Person model, and set the$fillablepropertybind your local implementations to the package's request validations and model in your local
AppServiceProvideruse LaravelEnso\People\app\Http\Requests\ValidatePersonStore; use App\Http\Requests\ValidatePersonStoreRequest as LocalPersonStore; use LaravelEnso\People\app\Http\Requests\ValidatePersonUpdate; use App\Http\Requests\ValidatePersonUpdateRequest as LocalPersonUpdate; public function boot() { $this->app->bind(ValidatePersonStore::class, function () { return new LocalPersonStore(); }); $this->app->bind(ValidatePersonUpdate::class, function () { return new LocalPersonUpdate(); }); $this->app->bind(EnsoPerson::class, function () { return new Person(); }); }
Publishes
php artisan vendor:publish --tag=people-config- configuration filephp artisan vendor:publish --tag=enso-config- a common alias for when wanting to update the config, once a newer version is released, usually used with the--forceflagphp artisan vendor:publish --tag=people-factory- the factory for thePersonmodelphp artisan vendor:publish --tag=enso-factories- a common alias for when wanting to update the factories, once a newer version is released, usually used with the--forceflag
Contributions
are welcome. Pull requests are great, but issues are good too.
License
This package is released under the MIT license.
← PDF Permissions →